Can machines think? We are talking about artificial intelligence, “the biggest myth of our time”!
A simple definition for AI could be: “a set of applied theories and techniques to create machines capable of simulating intelligence.” Among those AI functions, there is deep learning, an automated learning method used to process data.
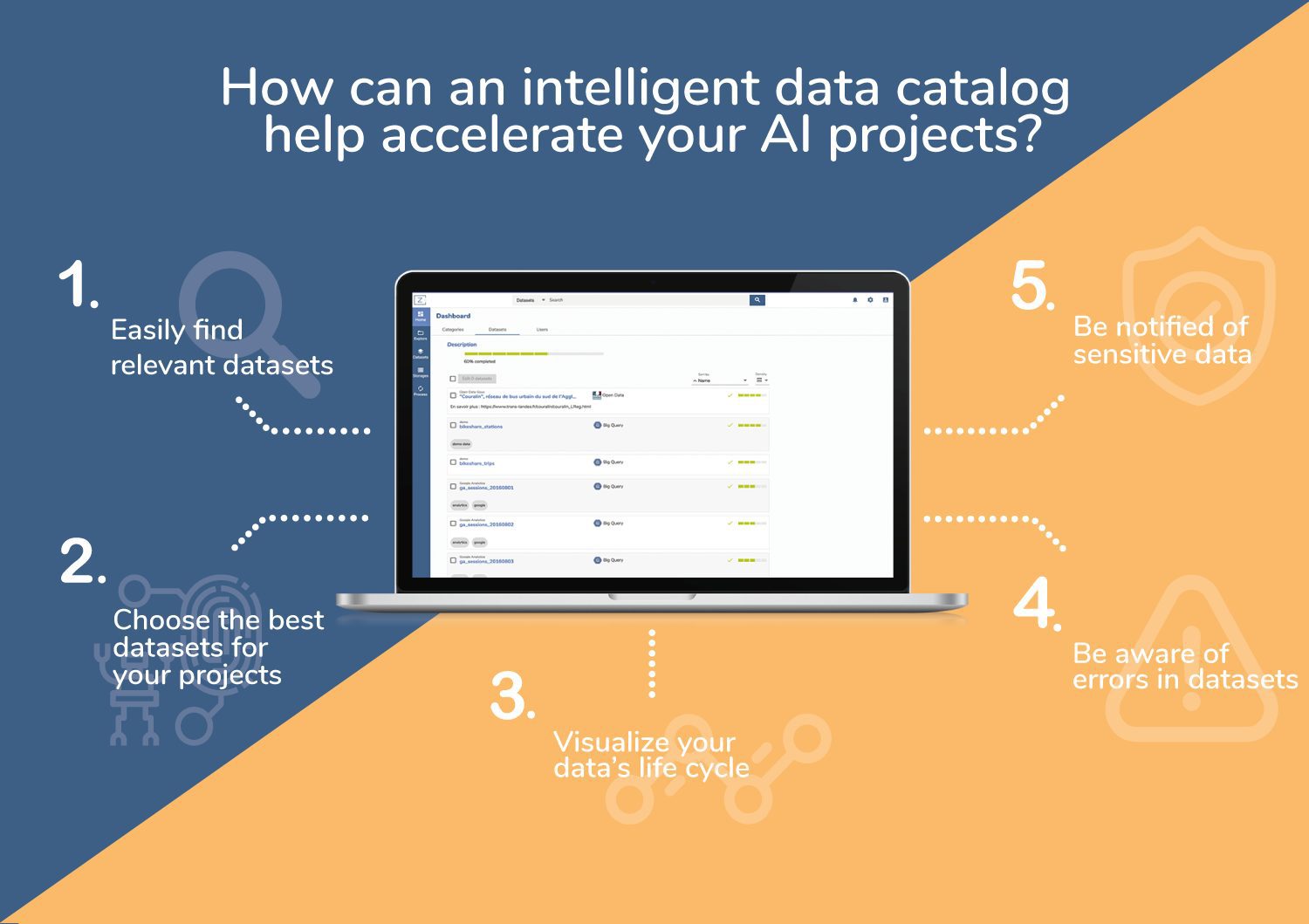
Data must be understood and accessible. It’s with the help of an intelligent data catalog that data users, such as data scientists, can easily research and efficiently choose the right datasets for their machine learning algorithms.
Let’s see how.
Search engine: facilitation dataset research
By connecting to all of an enterprise’s data sources, a data catalog can efficiently pull up a maximum amount of documentation (otherwise known as metadata) from its storage systems.
This information, indexed and filterable in Zeenea’s search engine, allows for data users to quickly attain the data sets needed for their information systems.
Recommendation system
Guiding Data Scientists in their choices
An intelligent data catalog is a tool that rests on “fingerprinting” technology. This intelligent feature gives recommendations to data users as to what data sets are the most relevant for their projects based on, among others:
- How the data is used,
- The quality and scoring of the documentation,
- Its previous searches,
- What other users search for.
- Give more meaning to their datasets
This feature offers data users that are responsible for a particular data set some suggestions as for its documentation. These recommendations can, for example, be associated with tags, contacts, or even business terms of other data sets based on:
- The analysis on the data itself (statistical analysis),
- The schema resembling other data sets,
- The links on the other data set’s fields.
- Automatically contextualizing data sets in a data catalog allows for any data user to work with data that is understood and appropriate for their use cases.
Automatic dataset linking: visualizing your data’s life cycle
As mentioned above, with fingerprinting technology, a data catalog can recognize and connect to other data sets. We are talking about data lineage: a visual representation of data life cycles.
Automatic error detection: be aware of errors in datasets
In order to overcome potential data interpretation problems, an intelligent data catalog must be able to automatically detect errors or misunderstandings in the quality and documentation of any data.
This key feature, based on the analysis of data or its documentation, must alert data users of its integrity.
GDPR notification: be notified of sensitive information
An intelligent data catalog must be able to detect personal/private data in any given data set and report it on its interface. This feature helps enterprises respond to the different GDPR demands put into place in May 2018, and also to alert potential users on the sensitivity level as well as the use of their data.